Agentic process automation (APA) then orchestrates RPA and AI agents that think, learn, and act across systems and collaborate with human workers to make decisions and drive outcomes, while RPA provides the execution layer agents can call on to perform tasks quickly and accurately at scale.
RPA excels at automating the types of repetitive tasks at the heart of so many enterprise processes. It’s valued for its reliability in automating high-volume, repetitive tasks such as extracting data, transferring data between applications, applying calculations and categorizations, connecting to APIs, scheduling meetings, tracking approvals, and other fundamental business tasks.
The origins of RPA can be seen in the keystroke macros developed for business applications in the 1990s. As RPA advanced, surrounding technologies advanced even faster, making many business processes far too complex for RPA’s rigid, rules-based structure.
While task-focused RPA accelerates and automates steps in larger processes, there are massive speed gains, accuracy improvements, and enterprise value in extending automation to more complex tasks, unstructured data, cognitive decision-making, and other elements that make up today’s end-to-end business processes.
More recently, intelligent automation paired RPA with AI to automate more complex processes, using AI to understand unstructured data and add decision-making and learning capabilities. Where RPA flags an exception, requires validation, or an automation is otherwise blocked, AI steps in to act across systems, process documents, interpret natural language, detect errors, and more.
Going further, APA orchestrates RPA and AI agents to complete even more complex end-to-end processes that involve decision-making and planning — even without continuous human supervision. Today, the autonomous enterprise is possible, and RPA remains a critical component of intelligent, agent-driven automation.
This article covers the definition of RPA, different types and categories of RPA, why APA and agentic AI enable a transformative leap in RPA’s value, and how Automation Anywhere offers a fast track to becoming an autonomous enterprise.
Types of RPA
One of RPA’s defining features is simplicity. Even non-technical workers can configure RPA-driven workflows without software development or coding skills, including building secure, governed, goal-driven AI agents that rely on RPA for task execution.
Enterprise-grade RPA also adds security, governance, integration, scalability, reliability, and compliance capabilities required by large organizations, including the ability to run thousands of automations simultaneously while ensuring high availability and performance.
RPA falls into three main categories:
- Unattended RPA automations use pre-programmed triggers, data inputs, and schedules to run independently, without human intervention. These automations are typically applied to back-office processes like data entry, IT operations, and application integrations and can be called on by agents and APA to execute discrete, repeatable tasks on demand.
- Attended RPA automations are initiated with triggers or inputs to help human workers with routine tasks on demand. These automations provide human workers with real-time assistance for interactive business processes such as customer service and IT helpdesk operations, retaining human-in-the-loop (HITL) oversight but evolving to enable orchestration by agents and APA.
- Hybrid RPA automations blend attended and unattended RPA, where automations and human workers interact and collaborate to complete tasks and processes. These automations are more adaptable to complex business processes and enable even more speed, accuracy, and efficiency when orchestrated to combine agentic and HITL decision-making.
The specific types of RPA have become less important with the advent of APA. Today, agentic orchestration coordinates RPA, AI agents, and human workers as needed and alerts them to make decisions, validate actions, and resolve exceptions. Even with continued innovation and evolution in automation technologies, enterprises continue to harness AI to work in tandem with RPA, and RPA remains crucial for automating larger, complex business processes to achieve mission-critical business goals.
Why RPA still matters in the age of AI process agents
Even in the age of AI, RPA provides an operational foundation that enables enterprise-wide, AI-driven automation while delivering proven, measurable business benefits right out of the gate. Businesses of all sizes use RPA to reduce costs, increase accuracy, increase speed, and more. As agentic AI and APA enable the autonomous enterprise, RPA tackles discrete tasks and increases productivity at every level.
Areas where RPA delivers measurable AI-enabled results driven by task-level efficiency include:
RPA increases enterprise speed without compromising security, compliance, or control
RPA automates high-volume, repetitive tasks with precision, enabling manual tasks that can take hours to be executed at near-instant speeds and high volumes. Since RPA is inherently rules-based, automations maintain strong security, compliance, and control measures by following policies and protocols exactly while generating a complete audit trail of actions.
Security is also bolstered via RPA by eliminating opportunities for human error or exposure of sensitive data. And, technology silos are overcome with RPA’s seamless integrations and speedy data transfers across software tools regardless of technology, function, or department.
RPA’s efficiency lowers operating costs and improves the worker experience, but its value grows immensely as RPA, human workers, and agentic AI are orchestrated across high-volume business processes.
RPA improves process and decision accuracy for faster innovation
RPA executes tasks without human intervention, eliminating the potential for human error. APA adds intelligent orchestration to employ AI agents to make decisions and handle exceptions with high accuracy, only calling on human workers for critical exceptions, validations, or decisions that require HITL oversight. The result is near-perfect process accuracy and data extraction accuracy, at scale, to improve downstream insights, decisions, and outcomes.
RPA automates mundane, repetitive, and error-prone work and processes, elevating human workers into strategic, higher-value decisions and activities that spark ideas and drive innovations. APA then orchestrates RPA with agentic AI to improve those decisions, ideas, and innovations by eliminating technology silos and seamlessly connecting software tools across the enterprise. This provides deeper, more accurate, and more useful information and insights to human workers.
RPA frees human workers to focus on rewarding, fulfilling, and valuable work like solving problems, building relationships, and innovating at all levels.
RPA accelerates enterprise scalability with effective governance
Effective governance ensures compliance, data privacy and security, and, ultimately, customer satisfaction. RPA automates tasks while adhering to strict, rules-based compliance standards, performing actions exactly as prescribed every time — and generating a complete, detailed audit trail of every action for end-to-end governance. Enterprises can then quickly scale automations confidently, knowing RPA executes tasks reliably and compliantly.
For complex and end-to-end processes, APA relies on RPA’s dependable, trusted execution to ensure strict adherence to policies and procedures, enabling APA to orchestrate agentic AI to accomplish broader, more complex goals without compromising trust. RPA remains a critical element of overall governance, and can even automate governance tasks such as tagging and classifying documents, extracting information from documents and systems, and transferring documents and information to locations specified by governance policies.
RPA enables repeatable, trusted, compliant execution of enterprise tasks, providing a governed automation foundation APA builds on to quickly scale automations enterprise-wide.
Enterprise automation use cases
RPA excels at executing manual and repetitive tasks like billing and coding invoices in finance or sending appointment reminders in healthcare delivery settings. For enterprises in nearly every industry, RPA is applied to automate time-consuming workflows such as data entry, customer service responses, report generation, and even email management. This delivers dramatic time and cost savings, frees employees for strategic work, and enables APA to orchestrate RPA along with AI agents and human workers to tackle end-to-end processes for increased automation ROI.
Examples of where RPA is used across industries include:
Financial Services
Financial services and banking processes rely on accuracy, security, and compliance — areas where RPA excels. Tasks automated with RPA include:
- Customer onboarding to speed up collecting and verifying customer information with RPA that cuts processing time and improves the customer experience.
- Loan processing automation, with RPA handling data entry and document checks for credit assessments, and supporting faster decisions with higher accuracy.
- Compliance and regulatory reporting, where RPA gathers and processes data to reduce the chance of human error and verify that requirements are met.
Adding APA and agentic AI expands the value for financial services, accelerating loan processing times from days to minutes, cutting transaction costs in half, and increasing customer satisfaction rates to over 90%. Representative use cases of APA and AI agent-driven automation in financial services include:
- Personalized financial advisory, where AI agents deliver tailored advice to clients.
- Fraud detection and prevention, where AI agents add real-time monitoring of transactions and customer behaviors to identify potential fraud quickly.
KeyBank, for example, uses RPA for mortgage quality checks but vastly increased the scale and value of RPA-based automations with APA: AI-powered data extraction enabled the bank to process over 40,000 documents — a workload that would’ve taken nine years manually — in just 14 days.
Healthcare
RPA can inject operational efficiency into healthcare processes, reducing administrative burden and enabling personalized patient care to ultimately improve outcomes. Top RPA use cases in healthcare include:
- Patient scheduling with RPA automating appointment bookings, reminders, and cancellations to improve patient access and drive down no-show rates.
- Claims processing using RPA to speed and shorten reimbursement cycles by automating the verification of patient information, claims submissions, and tracking follow-ups.
- Patient data management using RPA to extract and input data from multiple sources to update and validate information within electronic health records (EHR).
RPA tackles healthcare tasks that APA and AI agents build on to enhance care quality, ensure regulatory compliance, and transform how healthcare organizations operate and deliver care. Healthcare use cases for APA and agentic automation include:
- Medical data processing by AI agents that streamline the extraction, classification, and validation of data from electronic health records (EHRs), improving accuracy and efficiency in managing patient information.
- Clinical decision support from AI agents that assist physicians with diagnosis predictions and patient risk assessments, enabling more accurate and timely interventions.
The UK’s Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals network, for example, implemented RPA to save 7,000 hours per year. By automating highly repetitive human resources workloads, the network scaled document processing automation across multiple departments, freeing clinical staff from paperwork and giving them two additional days to prioritize patient care.
Manufacturing
From factory floor to back office, applying RPA to manufacturing operations reduces costs, improves productivity, and speeds time-to-market. Practical use cases for RPA in manufacturing include:
- Inventory management, where RPA can automate stock level monitoring, reorder processes, and inventory reconciliations to ensure optimal stock levels and reduce the risk of shortages or overstock.
- Order processing with RPA handling purchase orders, invoices, and shipment tracking autonomously, improving accuracy and fulfillment times
- Product inspections and quality control, automating data collection and analysis with RPA to ensure compliance with quality standards.
Agentic AI and APA add value to RPA-driven tasks in manufacturing by breaking down information silos across the industry’s ubiquitous enterprise resource planning (ERP), manufacturing execution systems (MES), quality management systems (QMS), and other legacy applications. Even more, APA orchestrates automations and human workers to increase efficiency and quality, reduce downtime, and improve resource optimization. Manufacturing use cases for APA and AI agents include:
- Minimizing downtime with early intervention, using AI agents to detect early warning signs in equipment performance and automatically schedule maintenance before issues escalate.
- Dynamic production planning, with AI agents deployed to incorporate real-time demand and supply chain shifts and keep production agile and efficient.
Stant uses APA to automate its invoice-matching process, reducing the invoice backlog from three weeks to just four days. With RPA handling tedious tasks like invoice matching and data entry, APA enhanced the automations to achieve 80% straight-through processing, including 94% processing on targeted supplier invoices and zero data entry errors.
Customer Service
RPA in customer service simultaneously increases operational efficiency and delights customers. It’s a common function in most enterprises, yet it still relies on repetitive, manual tasks to ensure customers’ needs are met promptly and accurately. Specific use cases for RPA in customer service include:
- Automated inquiry handling through chatbots or virtual assistants that employ RPA to respond to routine questions, such as requests for order status or account information, or direct more complex inquiries to the right agents.
- Ticketing and issue resolution use RPA to log customer complaints, categorize them, and route them to support teams, and reduce response times.
- New customer onboarding leverages RPA to automate data entry and verification for a faster, smoother customer experience.
Now, APA and agentic AI in customer service, along with generative AI, are evolving RPA to automate more customer interactions and deliver immediate yet personalized support. Where RPA uses scripted responses, agentic automation leaps ahead by understanding context and intent to interact conversationally and autonomously resolve inquiries, process transactions, and make decisions. APA and AI agent use cases in customer service include:
- Ticket management and escalation where AI-driven workflows categorize and prioritize support tickets, ensuring they reach the right agent based on complexity and urgency or are escalated to human agents.
- Sentiment detection and feedback analysis use AI agents to assess customer sentiment in real time, adjust responses, flag potential issues, and refine service approaches to improve the customer experience.
The City of Seattle had thousands of backlogged customer requests, with over 6,000 in its utility discount program alone. With the help of RPA, it eliminated the backlog and automated 700 daily password lockout requests, and more, saving over 30 hours per month. Building on that RPA foundation, the City of Seattle added Automation Anywhere’s Agentic Process Automation System to automate document processing and analytics, saving over 1,500 hours.
For every industry, RPA supports smarter, modern, agentic automations. Simple, repeatable tasks form the foundation of every business process. When orchestrated with other RPA, AI agents, and human workers using APA, the autonomous enterprise is truly possible.
How RPA fits into the agentic enterprise automation fabric
To build or manage an enterprise-wide agentic automation program, RPA serves as the execution layer that operates within AI-driven automation frameworks. RPA is an important element of the comprehensive automation fabric that spans process discovery, orchestration, and optimization. APA is the conductor that then orchestrates RPA, agentic AI, and human workers to collaborate effectively, integrate seamlessly with enterprise systems, and manage workloads.
Even in today’s fast-paced, AI-fueled environment, RPA remains integral to the autonomous enterprise, serving as the core mechanism for automating work alongside pre-built integrations and API connectors. It acts as the "arms and legs" of automation within a larger AI-driven automation framework that powers the discovery of workflows, the development of automations, and the sourcing of the necessary data to drive automated operations.
How AI and agents are transforming enterprise automation
RPA has come a long way in a short time. By automating repetitive, high-volume tasks like data entry, scraping, and extraction with low-code, easy-to-adopt automation tools, RPA breaks down long-standing productivity barriers.
This RPA-led foundation for the autonomous enterprise enables today’s APA and agentic AI, combining RPA with cognitive technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and fuzzy logic. This combination of AI and RPA, termed intelligent automation, marked an important step in the evolution of RPA and the creation of APA.
The role of generative AI in the RPA evolution
The advent of generative AI builds on RPA and other AI technologies to enable even faster, easier automation development and interaction, such as natural-language automation assistance, automated generation of functional automations, and resilient, self-healing automations. AI now enables RPA to automatically recover from changes to underlying applications, reducing execution failures by over 50%.
Generative AI is also the engine of AI agents, a significant technology advancement harnessing the cognitive capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to make decisions, learn from data, interact with humans through natural language, and ultimately take action to achieve goals. Enabling action requires connecting AI agents with applications and systems where they can get work done, such as sending an email or saving a report. At the process level, agentic workflows can use RPA to execute tasks quickly and accurately.
The rise of APA platforms
New APA platforms use RPA and agentic AI to build, deploy, and manage AI agents easily. Architected for enterprise privacy, security, and compliance, APA platforms address the governance needs and complexities of enterprise deployments, including orchestrating thousands of automations with central management and oversight.
APA enables agentic workflows — RPA, AI agents, and humans working collaboratively and connecting with other AI agents to perform end-to-end processes as part of multi-agent systems that are forever changing the face of enterprise automation.
Deploying RPA as part of an agentic automation strategy
Organizations on the journey to the autonomous enterprise have a wealth of resources and expertise to draw on, along with a growing list of best practices gleaned from standout RPA and APA implementations by both industry analysts and solution providers.
For those looking to accelerate the process, here are prescriptive steps for deploying automation:
Engage stakeholders early and align with business goals
Put human workers’ needs at the center of planning, bring in HR early, and involve a broad cross-section of stakeholders, leaders, and automation champions who can influence change. Diverse input will help shape a robust, inclusive strategy that boosts adoption, so ask lots of questions — both internally and externally. Reach out to trusted partners, vendors, and other organizations already on the path to becoming an autonomous enterprise.
Establish a center of excellence (CoE) for standards and governance
Start strong by creating an organization-wide center of excellence (CoE). The CoE should focus on effectiveness and governance and will be responsible for developing standards to ensure compliance, security, and continuous improvement across the automation life cycle.
Design the CoE as a hub of expertise, established to help the entire organization get up and running with consistent, high-quality automations by propagating best practices, tools, and templates.
Select an enterprise-ready, scalable platform with agentic process automation
Choose a vendor that aligns with your long-term automation and business goals. APA's success hinges on workforce adoption, which means selecting software that is both technically robust and user-friendly for all employees, not just IT specialists. Key considerations include:
- Pricing model: Transparent cost structures help you avoid unexpected expenses as your APA deployment scales. Look for flexibility in pricing, including options for unlimited bot usage.
- Innovation: APA and AI technologies are rapidly evolving. Look for vendors with proven experience and stability and that are committed to continuous innovation. Prioritize vendors with dedicated teams focused on evolving RPA and advancing APA capabilities, including migration tools, orchestration, and AI integration.
- Support: Robust customer support, comprehensive training programs, and active community engagement will enable a successful automation journey.
- Security: One of the core benefits of APA is strengthening security, which relies on the security architecture and certifications a solution adheres to. If relevant, consider vendors that offer vertical-specific solutions for industries with stringent data security requirements, such as government, financial services, and healthcare.
- Flexibility: Select solutions that enable RPA, agentic AI, and full APA orchestration for flexibility in task execution and complex, end-to-end process automation. APA should also integrate seamlessly with existing systems, including legacy applications and cloud services. Choose vendors that invest in AI-driven features to improve automation efficiency and adaptability.
- Accessibility: Consider APA platforms that offer low-code or no-code development options that enable technical and non-technical users to easily create and use RPA- and AI-driven automations. Look for training and tools that encourage adoption yet maintain IT oversight to ensure quality, security, and governance.
- Scale: Design automations with growth in mind. Even if beginning with small pilots, ensure that platform infrastructure, licenses, and governance frameworks can adapt as automation needs expand. Look for solutions that dynamically scale to accommodate increasing workloads and user demands without compromising performance.
Start small with high-ROI use cases; scale iteratively
Determine which processes will yield the greatest ROI through automation. Many enterprises choose to start small, automating tasks that are part of a larger process. RPA applied in this way is referred to as attended automation; it allows workers to become familiar with automations firsthand while providing a foundation for eventually using APA and AI agents to automate more complex tasks and processes.
Measure KPIs (ROI, adoption rate, uptime) to track success
Whether it’s RPA automating a simple task or APA orchestrating AI agents and human workers to automate an end-to-end, mission-critical process, track automation performance, uptime, and ROI. This data is crucial to optimizing processes and refining automation strategies. Ensure APA solutions include management features for monitoring, configuration, and governance of automated processes. Regularly gather user and stakeholder feedback to refine automations and address post-deployment opportunities and challenges.
Evolve from RPA-driven tasks to APA that orchestrates end-to-end processes
RPA might be the automation entry point, but APA is the goal. Make sure any RPA is part of a complete agentic automation fabric that considers everything from APIs to agents to analytics. This ensures RPA remains instantly adaptable, infinitely scalable, and always up to date in the journey to becoming an autonomous enterprise.
Challenges and considerations for scaling RPA
RPA solutions are ubiquitous across enterprise environments, with decades of experience available to streamline and ensure the reliability of RPA deployments. Nevertheless, some organizations may have unique operating environments or niche business needs that create challenges for RPA efforts or encounter roadblocks as they mature beyond RPA into agentic AI and APA. Thoroughly assessing business needs, considering AI-era opportunities, and proactively addressing potential roadblocks as automations are developed can help ensure a path to RPA success.
Process discovery and optimization
Enterprises often struggle to accurately identify and map existing processes or face challenges when attempting to optimize them due to a lack of visibility into process nuances and bottlenecks. This can lead to missed automation opportunities — for RPA deployments and more modern APA initiatives.
Process challenges can easily be overcome by selecting an automation platform with integrated AI tools for discovering, documenting, and visualizing processes granularly. Automation Anywhere offers AI-powered process discovery insights that reveal how work really gets done, helping organizations identify, understand, capture, and optimize processes across the enterprise.
Data structuring
Without APA and AI-derived insights, RPA can only operate effectively with structured data. Unfortunately, most business data is in unstructured formats, like emails and documents. This limits RPA effectiveness and pushes more exceptions to human workers for evaluation and rework.
Agentic AI understands unstructured data, captures and organizes information, and injects relevant data into RPA and AI-driven automation workflows. Automation Anywhere’s Document Automation uses natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, generative AI, large language models (LLMs), and machine learning (ML) to accelerate document classification, data extraction, and validation across any document type.
Governance
A lack of governance models can lead to automation inconsistencies that undercut scalability, whether those automations are RPA- or AI-driven.
Effective governance ensures the reliability, compliance, and operational effectiveness of automation programs, supporting scalability and helping to protect organizations and their customers from risks like disruptions and data breaches. Automation Anywhere’s CoE Manager centralizes oversight from the earliest stages of process discovery through ongoing ROI, with guardrails, visibility, and clarity that ease governance and compliance.
Maintenance and resilience
Enterprises may not have enough skilled personnel to maintain RPA. That challenge is exacerbated as organizations rush to deploy APA and agentic AI automations, and as business applications advance and evolve in ways that disrupt rigid, rules-based RPA. Without the right skills, enterprises face automation downtime, costly reliance on external resources, and risky workarounds.
New tools use generative AI to recognize changes and update automations quickly. Automation Anywhere’s Automator AI lets organizations build self-repairing, reusable automations that adapt to application UI changes to reduce automation maintenance costs.
RPA vendor landscape and market overview
Automation technology is a fast-moving market. AI-driven advancements and specialty solutions have driven rapid proliferation in vendors and features. While the RPA vendor landscape remains active, market leaders like Automation Anywhere have evolved beyond RPA into full APA platforms.
Analysts covering the RPA, agentic AI, and APA spaces project continued enterprise enthusiasm for automation technologies at all levels. Gartner reports 14.5% growth for the RPA software market, while IDC says, “Over the next several years, AI agents combined with orchestration and human-in-the-loop interactivity with copilots will largely disrupt how our enterprise processes operate.”
Specific enterprise automation solutions have maintained consistent market leadership across RPA while showing innovation in agentic AI-driven automation and APA. For example, Automation Anywhere has been named a “Leader” seven consecutive years in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for automation (2025). The IDC MarketScape for Business Automation Platforms 2025 also noted Automation Anywhere’s strong RPA capabilities and strong vision for agentic automation capabilities, stating, "Organizations heavily focused on executing an automation strategy or focused on agentic process automation should consider Automation Anywhere."
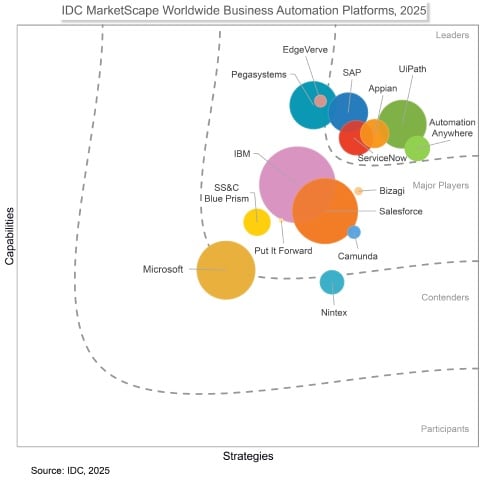
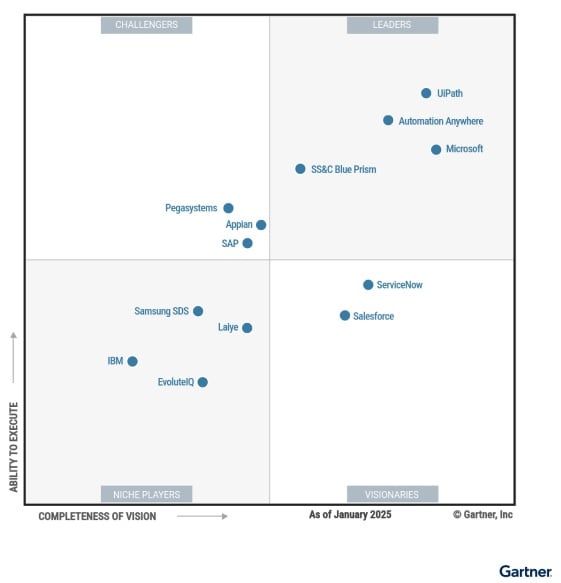
Enterprise solutions
Automation Anywhere, UiPath, and other enterprise-focused vendors develop solutions specifically designed for enterprise requirements, featuring extensive integrations and partner ecosystems, robust training programs, and the scalability to support enterprise use cases. Importantly, enterprise solutions include powerful agentic AI capabilities that build on RPA’s execution strengths to help automate complex, dynamic business processes.
Ecosystem-based solutions
ServiceNow, Salesforce, and SAP offer tools purpose-built to integrate with their own ecosystems, making them less suitable as standalone solutions and with less comprehensive offerings than enterprise solutions.
Specialty solutions
IBM and Nintex focus on specific regions, and their solutions center around workflow automation. They may have notable feature gaps compared to enterprise solutions, often lacking essential pieces for enterprise deployments, such as compliance support or a marketplace for development tools.
How Automation Anywhere powers the autonomous enterprise
RPA-based automation is transforming enterprises across all industries. With agentic AI and APA, automation now takes on tasks that require decision-making. This extends automations beyond what was previously possible, enabling up to 80% of mission-critical, cross-functional processes to be automated.
This rapid innovation in APA makes the autonomous enterprise possible with a complete, cohesive, and holistic agentic AI-powered automation fabric, from RPA to APIs, agents to analytics, legacy systems to cloud applications.
Automation Anywhere was the first to launch APA, and its Agentic Process Automation System is already delivering hundreds of millions of dollars in benefits to top enterprises in banking, healthcare, manufacturing, and other industries.
Agentic process automation
APA relies on traditional, rules-based automations plus more adaptive, intelligent components, allowing business processes to flow as human workers, agentic AI, and RPA collaborate to complete tasks in pursuit of greater goals. The strength of Automation Anywhere’s Agentic Process Automation System lies in how it integrates and orchestrates this fabric of automation technologies, multi-agent systems, legacy applications, and human workers, along with governance, analytics, and more — all from a single, seamless enterprise automation platform.
Governance and trust
Trust is a requirement for enterprise automation as AI agents and APA work independently on mission-critical processes that are sometimes unpredictable. Enterprises must expect compliance and risk mitigation from RPA through APA. Automation Anywhere provides AI guardrails to ensure safety, compliance, and alignment with enterprise standards, with auditability to monitor automation performance and benchmarking to deliver automation accuracy, consistency, and performance at scale.
Business impact and case studies
- KPMG, a global provider of independent audit, tax, and advisory services, set out to streamline operations, eliminate inefficiencies, and reduce workload. Using Automation Anywhere, KPMG combined Document Automation and AI agents to automate knowledge gathering and creation of new learning experiences, all orchestrated using the Agentic Process Automation System. The firm has already realized a $90 million impact from agentic AI and has identified another $150 million in potential APA impact as it scales agentic automation across its organization.
- Cargill, an agricultural solutions and industrial products provider, receives thousands of orders in different formats, creating a chaotic, manual process that delays shipments, frustrates customers, and puts future orders at risk. With Automation Anywhere’s Agentic Process Automation System, Cargill automated 70% of its order processing workflow to slash cycle times to less than one minute per order. The resulting efficiency boost saves the company $15 million annually, while also improving the experience for customers and workers.
- Petrobras, a South American energy company, wanted to expand its use of AI and automation enterprise-wide. Beginning with tax accounting and the company’s $54 billion annual tax payment, Petrobras used Automation Anywhere’s Agentic Process Automation System to automate tax calculations, processes, and filings to save $120 million and increase efficiency by 40%. The company also identified more than $1 billion in additional potential savings as it works to scale APA across its organization.
Your organization could be an autonomous enterprise, too. Learn more about Automation Anywhere’s Agentic Process Automation System, and request a demo to see how the Agentic Process Automation System can automate up to 80% of enterprise business processes.
Frequently asked questions.
What differentiates RPA from AI agents?
RPA quickly and reliably automates rules-based digital tasks such as extracting data, transferring data between applications, and scheduling meetings. AI agents are action-enabled AI-powered assistants that work autonomously to achieve defined goals, such as suggesting driving routes and resetting customer passwords. AI agents rely on RPA to provide the execution layer that performs tasks quickly and accurately at scale.
Is RPA still relevant if we’re moving toward an autonomous enterprise?
RPA is a critical component of the autonomous enterprise, since it executes business processes at scale with speed and accuracy. Nearly every enterprise process involves repetitive tasks such as data extraction, form filling, and data transfers between applications. RPA integrates with enterprise systems to execute these tasks across applications so agentic AI and APA can make decisions and orchestrate RPA, human workers, and agents to automate complex processes and enable the autonomous enterprise.
How does RPA evolve into agentic orchestration?
RPA is a foundational building block that enables agentic orchestration to automate complex, end-to-end processes. RPA handles repeatable, rules-based tasks while agentic AI, APA, and human workers manage cognitive, decision-based tasks and task exceptions. As automation has evolved into an AI-driven technology, RPA remains at the core to complete task-level actions that enable automation of larger processes.
What role does RPA play in the autonomous enterprise?
RPA is the execution layer of the autonomous enterprise, completing the high-volume, repetitive digital tasks at the heart of many enterprise processes. APA and AI agents leverage RPA to handle those tasks quickly and accurately, while APA orchestrates AI agents and human workers to accomplish higher-level tasks and make key decisions. Every component — human workers, RPA, agentic AI, and APA orchestration — is critical to the success of the autonomous enterprise.
What challenges do enterprises face when scaling RPA?
RPA’s success stems from its simplicity and scalability. However, enterprises sometimes encounter challenges in integrations with existing legacy systems, a lack of proper governance and oversight, and security concerns. Choosing an RPA vendor with strengths in these areas and proven success in deploying and scaling RPA will help overcome these and other automation challenges.
How has Automation Anywhere helped global enterprises achieve ROI with RPA?
Over 1,500 automation deployments depend on Automation Anywhere solutions, with RPA being at the heart of every automation. Global enterprises achieving ROI with RPA include Bancolombia, reducing provisioning costs by $19 million, Osaic, realizing a 186% ROI in year one, and Ricoh, saving €100,000 and 500 days per month.
How does Automation Anywhere ensure governance and security in automation?
Automation Anywhere centralizes oversight for all stages of automation with capabilities for guardrails, visibility, and clarity that monitor automations and ease governance and compliance. Its solutions also integrate AI throughout to prioritize built-in security measures, enable responsible AI frameworks, and give customers clarity, control, and oversight over their data.