- Login
- Search
- Contact Us
-
Have a question? Our team is here to help guide you on your automation journey.
-
Explore support plans designed to match your business requirements.
-
How can we help you?
-
- AI
AI Without the Hype From pilot to full deployment, our experts partner with you to ensure real, repeatable results. Get Started
- Automation Anywhere AI
-
- Solutions
Featured Agentic Solutions
Accounts Payable Invoice automation—No setup. No code. Just results. Accounts Payable
Customer Onboarding Scale KYC/AML workflows. Customer Onboarding
Customer Support Keep queues moving, even at peak load. Customer Support
Healthcare RCM Revenue cycle management that runs itself. Healthcare RCM
- Products
Platform Features
- Agentic process automation (APA)
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- View all Products
-
- Resources
Get Community Edition: Start automating instantly with FREE access to full-featured automation with Cloud Community Edition.
Featured
 Named a 2025 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ Leader for RPA.Recognized as a Leader for the Seventh Year in a Row Download report Download report
Named a 2025 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ Leader for RPA.Recognized as a Leader for the Seventh Year in a Row Download report Download report- Become an Expert
- Developer Tools
- Get Support
- View all resources
-
- Partners
Find an Automation Anywhere Partner Explore our global network of trusted partners to support your Automation journey Find a Partner Find a Partner
- Find a Partner
- For Partners
-
Blog
Humanity: The Key to Addressing 3 Common Automation Challenges
Share this:
Navigate to content
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a kind of technology that allows a software program to execute repetitive tasks while using other software. It enables users to set up their own rules and conditions. Software can then register those actions and repeat them indefinitely when specific conditions are triggered.
Although this can provide useful assistance to white-collar workers who perform business processes, it’s something far from a human contribution in the workplace, representing a deterministic form of business process management.
Over the past few years, we’ve seen the advancement of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and analytics. With deep learning, you can train a neural network to mimic the human brain (just mimic, please) and, with machine learning, you can analyze huge amounts of data to find patterns that inform good decisions.
The strong advancements of these technologies are pervasive, and companies need to harness them to improve their operations.
What is intelligent automation?
The infusion of AI and analytics into RPA operations can create something amazing: intelligent automation (IA).
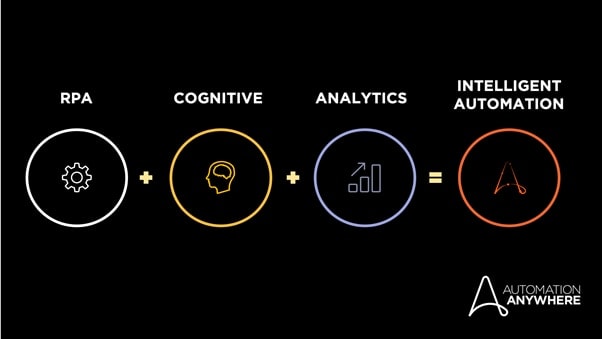
IA refers to a mixture of technologies that allow software to act in a smart way or, even better, execute repetitive tasks they’re not specifically programmed to execute by reacting to events and choosing the best operations for the situation.
Moreover, IA can orchestrate resources and become a sort of company backbone. Those resources can be humans, things, or tasks.
These big shifts and innovations are driving the digital “workforce” transformation. In order to reap the greatest benefit, companies must be aware of and plan for this transformation. But, as with any good thing, there are also challenges and points of failure involved. Let’s look at three of the most common:
1. Intelligent automation needs data governance
IA requires a lot of data to perform smart operations. Companies need to focus on data as an asset and not only as alphanumeric fields. Data governance — a mix of rules and tools designed to improve integrity, availability, and data readiness — is a must. Data governance is both a challenge and a potential point of failure.
2. You’re facing a new generation of algorithms
Normal software is deterministic and can’t think for itself. It can only execute a fixed rule, such as “if this, then that.”
IA uses a different kind of software that mimics the human thinking process to solve a problem — and then makes a decision in a probabilistic way. As a result, it’s a better investment to hire a data scientist than a programmer.
3. Human workforce reskilling
We previously mentioned the so-called digital “workforce” transformation, but what exactly does that mean? In the Industry 4.0 era, automation has come also to the workplace. Although this phenomenon involves the sunset of many human jobs, it will simultaneously prompt the sunrise of many new ones.
Necessary skills for the future of work
So, the million-dollar question is: What skills are needed to face this epochal change in the industry, and how will humans create value in an increasingly automated world?
Soft skills are a very important foundation to build upon. For example, let’s think about problem-solving: It’s true IA can solve some problems that humans can’t. However, when problems aren’t fully defined, humans can use their reasoning skills to figure out a solution that machines wouldn’t be able to find.
Moreover, the ability to collaborate and brainstorm to create new ideas is a feature that can boost business processes and optimize performances — and it has nothing to do with robots. These are human skills and represent the added value that automation simply can’t offer.
Thus, companies should focus over the next decade on the fact that, although machines will gradually become more powerful, humans will actually be even more essential, since technology will act as an integrator and not as a replacement for skills needed.
The jobs of the future will require a reskilling of the human workforce. The answer to digital disruption lies in our ability to apply humanity to the new challenges that arise.
Learn more about intelligent
automation.
About Antonio Grasso
Antonio Grasso is a digital transformation advisor, enterprise and public sector consultant, and mentor to numerous startups and large multinational companies.
Subscribe via Email View All Posts LinkedInGet to know the Agentic Process Automation System.

For Students & Developers
Start automating instantly with FREE access to full-featured automation with Cloud Community Edition.



